Dandruff is a skin condition that is difficult to hide and is an issue that affects roughly 50% of the adults world’s population. If you suffer or know someone who suffers from a form of dandruff, it’s important to know about its causes and – most importantly – that it can be controlled.
What Is It?
WHAT IS DANDRUFF?
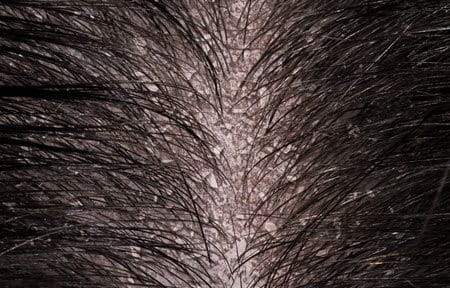
Dandruff is a very common scalp condition that comes in two forms. Greasy dandruff or seborrhoeic dermatitis occurs when oily and yellow flakes or scales form on your scalp and stick to your head and hair. Dry dandruff occurs when dry, white and loose flakes or scales form on your scalp and fall from your head and hair. Other symptoms can include itching, redness, and a greasy or dry scalp.
Major Causes
MAJOR CAUSES OF DANDRUFF
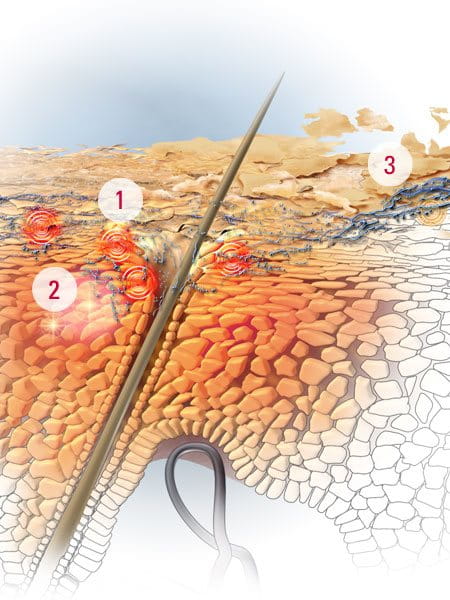
Dandruff occurs when your scalp’s cell renewal process shortens, leading to the rapid shedding of your scalp’s horny skin cells, which stick together to form visible flakes.
This process – known as skin hyperproliferation – is triggered by a micro-organism called Malassezia globosa, which thrives on the natural lipids or oils produced by your scalp. It’s this micro-organism that irritates your scalp, causing microinflammations and scalp itchiness.
All of the above can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
- Genetic predisposition – dandruff tends to run in families
- Climatic conditions – e.g. sun exposure, cold, heat, wind
- Physical or emotional stress
- Hormonal changes
- Lifestyle factors, such as diet or alcohol intake
Microinflamations and your scalp
What are microinflammations? They’re mild inflammations of the skin. They’re so mild, in fact, that even clinical testing won’t pick them up. But if we study skin tissue encountering microinflammations, we can detect the presence of inflammatory immune cells – in other words, the skin is responding to irritation with inflammation and thereby attempting to repair itself. If these skin cells are then subjected to further irritation, the skin can flip into a “true” inflammatory response.
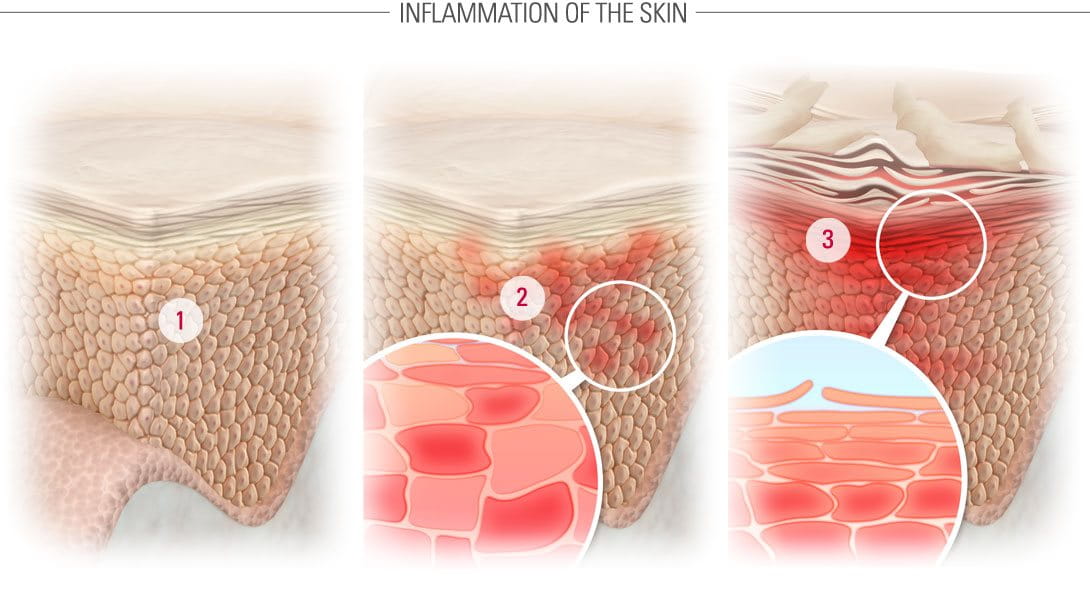
How are they related to scalp conditions?
There’s growing evidence that microinflammations of the scalp are involved in most common scalp disorders – from thinning hair and dandruff, to scalp dryness, itchiness and sensitivity.
If you experience sudden hair loss or brittle hair, you may have an underlying health problem such as thyroid disease, iron deficiency, or an autoimmune disease. Some medications can also cause hair loss. Contact a dermatologist in all instances to get further information.
Common Myths

- Dandruff can lead to thinning hair or hair loss
- Dandruff means your hair and scalp are dirty
- Dandruff can be treated with vinegars, natural oils or baby shampoo
There’s no evidence to suggest any of the above is true.
Solutions
RECOMMENDED SOLUTION

Use Eucerin DermoCapillaire ANTI-DANDRUFF GEL SHAMPOO for greasy dandruff or Eucerin DermoCapillaire ANTI-DANDRUFF CREME SHAMPOO for dry dandruff to wash out flakes without irritating your scalp.
Follow with Eucerin DermoCapillaire ANTI-DANDRUFF SCALP TREATMENT for a regimen that’s clinically and dermatologically proven to fight dandruff.
DO YOU HAVE DANDRUFF?
You may have dandruff if…
You have greasy yellow or white flakes that stick to your hair and scalp: This is typical of greasy dandruff or seborrhoeic dermatitis.
You have dry white flakes that fall from your hair and scalp: This is typical of dry dandruff.
You’re experiencing scalp itchiness or irritation, as well as visible flaking or scaling: Many people with greasy and dry dandruff experience these symptoms too.
You may have another scalp condition if…
You have dryness, itching or irritation, but no visible flakes: You may have a dry, itchy or sensitive scalp.
You have red, scaly, silvery-looking patches on your scalp: You may have Psoriasis.
Attention
See your doctor or your dermatologist if you’re concerned, your symptoms are severe, or your scalp becomes inflamed, weepy or sore.
Our brand values

We deliver a holistic dermo-cosmetic approach to protect your skin, keep it healthy and radiant.

For over 100 years, we have dedicated ourselves to researching and innovating in the field of skin science. We believe in creating active ingredients and soothing formulas with high tolerability that work to help you live your life better each day.

We work together with leading dermatologist and pharmacist partners around the world to create innovative and effective skincare products they can trust and recommend.







