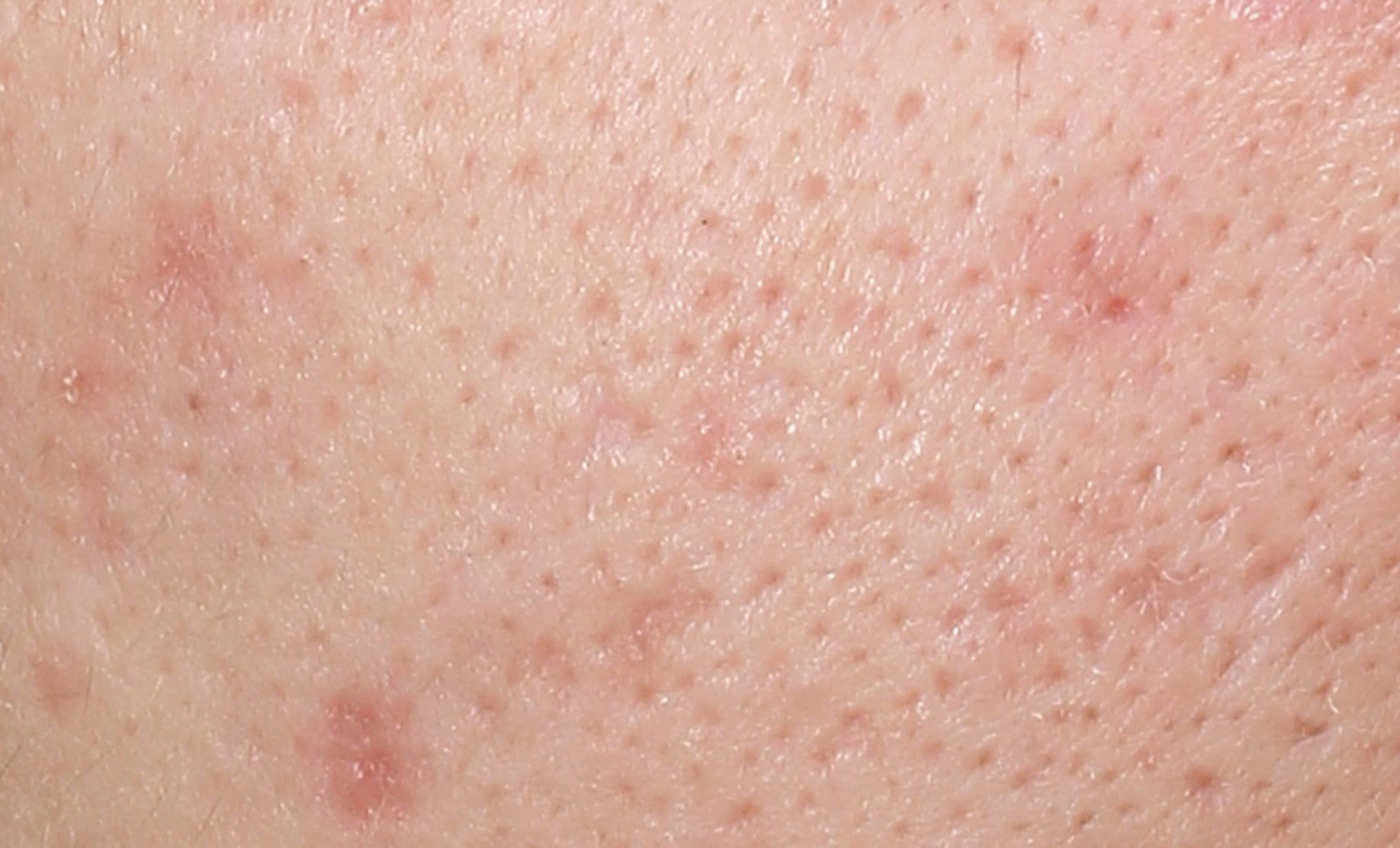
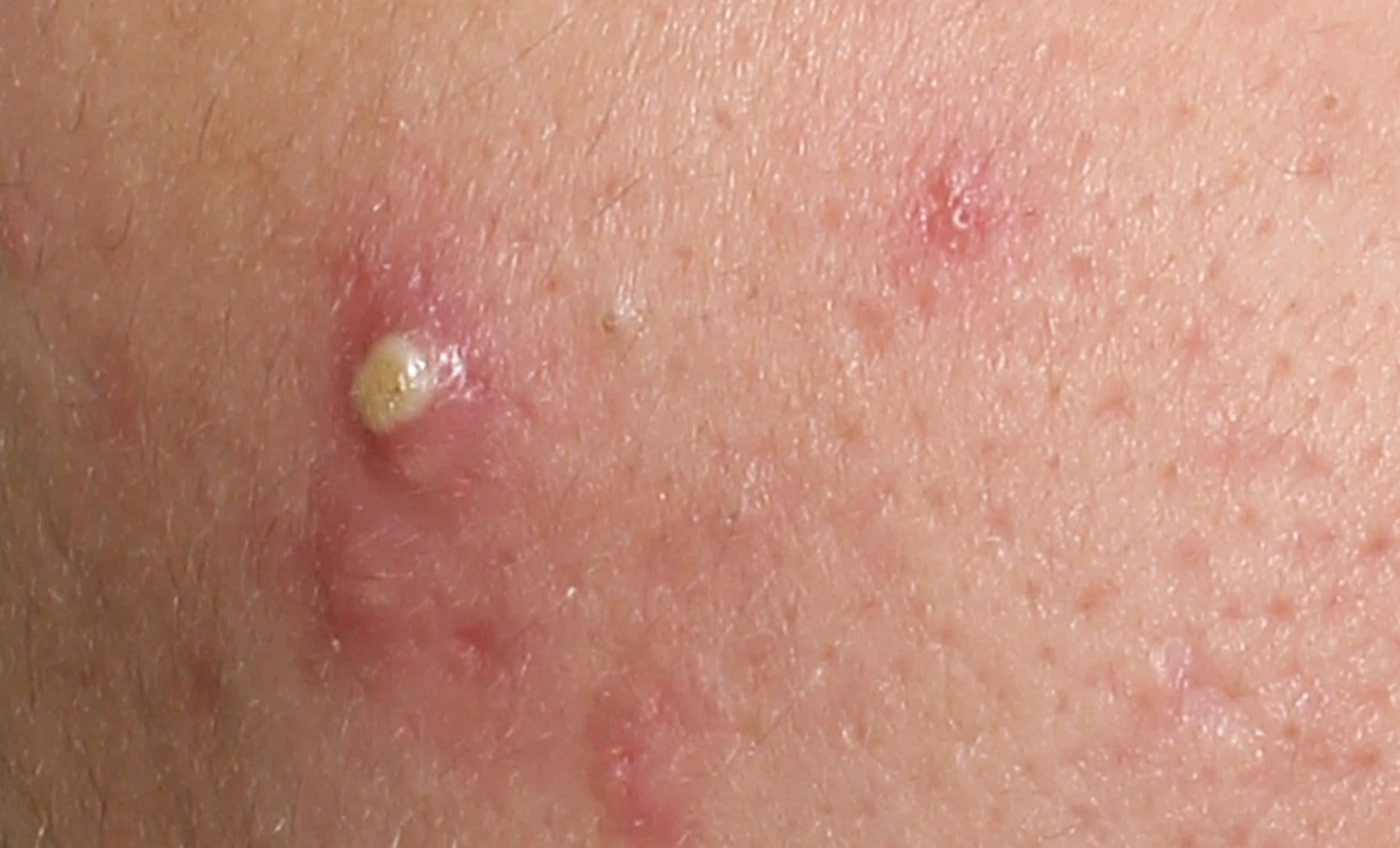
What are post-acne marks (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or PIH for short)?
PIH is a type of hyperpigmentation of the skin that is mainly triggered by the way skin regenerates after inflammation. It can affect the face and body, typically especially UV-exposed areas, and appears as flat spots of hypercoloration. These range in color from pink to red, brown or black, depending on skin tone and the depth of hypercoloration. The root cause is increased melanin production, the pigment that defines the color of a person’s skin, which is stimulated by inflammatory factors. The blemish triggers melanocytes – the melanin-producing cells – to release excessive melanosomes (pigment granules). The excessive pigment granules darken and discolor the formerly stressed area. Once initial blemishes have subsided, spots of hypercoloration, so-called post-acne marks, can remain.
Additionally, sun exposure can aggravate PIH symptoms, darkening the affected patches and prolonging the time it takes for them to fade. Most acne-related PIH will eventually fade over time, but it can take several years or even a decade until it is fully gone*.
*Abad-Casintahan, F. et al., “Frequency and Characteristics of Acne-Related Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation.” J Dermatol. 2016; 43:826–828.
Who is affected by post-acne marks?
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is common among many acne sufferers since a root cause for acne is inflammation. Those post-acne marks left behind after blemishes subsided can be even more aggravating and emotionally distressing than acne itself. Men and women are equally susceptible, and all skin types can get post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, although it is more prevalent in darker tones of skin, with over 65% of the Black Americans experiencing it, followed by 53% of Hispanics, 47% of Asians and 25% of Caucasians*. This means that we need effective and tolerable skincare fighting both blemishes and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation for consumers all over the world.
* Kaufman et al., Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018; 19:489–503, Perkins et al., JEADV. 2011; 25(9):1054–1060.
What is so special about Thiamidol?
Thiamidol is an exclusive and patented active ingredient developed during a 10-year research project. It reduces post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation by addressing the root cause, the production of melanin in the skin. Many known ingredients have undergone testing on mushroom enzymes alone rather than on human skin enzymes. The efficacy of Thiamidol in our Eucerin® Dermopure Triple Action has been demonstrated in real-life testing. Clinical trials* and other responses have shown that our formulation effectively reduces post-acne marks.
*Clinical efficacy study, 12 weeks, 2× daily use, 40 female and male patients, 18–40 years of age.
Beyond Thiamidol, what makes the DermoPure Triple Effect Serum so effective on blemish-prone skin with post-acne marks?
In addition to Thiamidol to reduce persistent post-acne marks and prevent their appearance, it contains salicylic acid to reduce blemishes as well as licochalcone A to prevent new blemishes from appearing. Thanks to the sebum regulation technology, the formulation leaves the skin with a long-lasting, matte and non-shiny look.