Over-exposure to the sun is the main cause of premature skin ageing, known as photoaging or sun-damaged skin. The sun’s UVA rays are primarily responsible, but high-energy visible (HEVIS) light can also cause oxidative stress that damages cellular DNA. As a result, skin starts to form wrinkles, sag, and develop pigmentation issues before its time. Ensuring skin is adequately protected year-round and using superior sun care products can help prevent photoaging.
What is photoaging?
When skin ages prematurely, it develops signs of ageing faster than expected. Research shows that up to 90% of all symptoms of premature skin ageing are caused by UV exposure1.
1 Ramos-e-Silva et al., ‘Anti-ageing cosmetics: Facts and controversies’. Clin Dermatol. 2013 Nov-Dec; 31(6): 750-8.
What is the difference between general skin ageing and premature skin ageing?
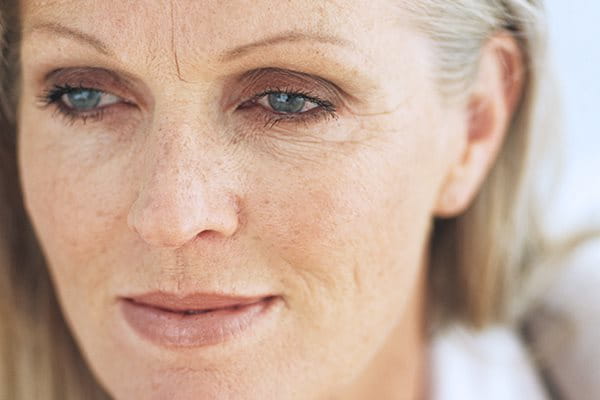

As skin ages, it changes:
- Collagen and elastin, responsible for the plumpness of youthful skin, begin to decline, and the skin loses volume and begins to sag, developing fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin is less able to attract and retain the moisture it needs, and the skin’s own production of Natural Moisturising Factors depletes. It becomes drier.
- It can develop uneven pigmentation, such as dark spots known as hyperpigmentation, a form of which is solar lentigines (more commonly known as age spots or sun spots).
You can find out more about how skin changes over the years.
There are two types of skin ageing − intrinsic and extrinsic:
Intrinsic ageing
Extrinsic ageing

What are the signs & symptoms of photoaging?

Photoaging or sun-damaged skin can cause symptoms and visible changes due to prolonged time spent outside without sun protection. UV light damages your skin, and over time, this can build up and cause changes that make you appear older.
These include:
What causes photoaging?
The photons in the sun’s UVB & UVA are two kinds of UV light which are directly attributed to sun-damaged skin, and they are classified as such below:
UVB:
- The photons in the sun’s UVB rays are absorbed by skin cells and cause direct damage to cellular DNA. UVB is what causes our skin to burn in the sun, and the direct DNA damage can also lead to skin diseases, including skin cancer.
UVA:
- While this direct DNA damage plays a part in photoaging of the skin, it’s the sun’s UVA rays that are the leading cause of premature skin ageing. UVA rays also damage cellular DNA, but they do so indirectly: they trigger the formation of free radicals, and it’s these free radicals that damage our DNA in a process known as oxidative stress.
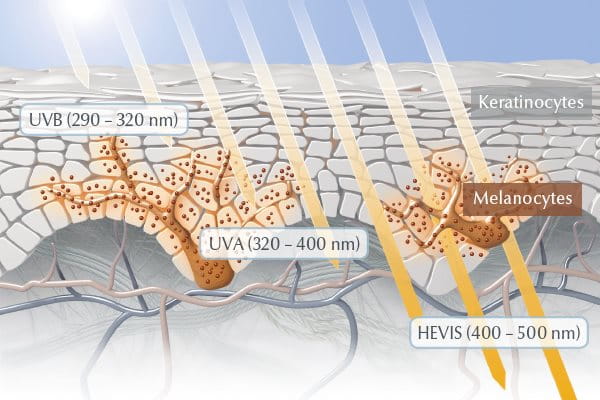
UVA rays are less intense than UVB, but they are 30 to 50 times more prevalent and are present at relatively equal intensity throughout all daylight hours throughout the year, so it is important to apply sun protection daily, year-round, to prevent sun damage to the skin. We also recommend that you look out for sun care products that include protection from HEV light.
How can I protect my skin from photoaging?


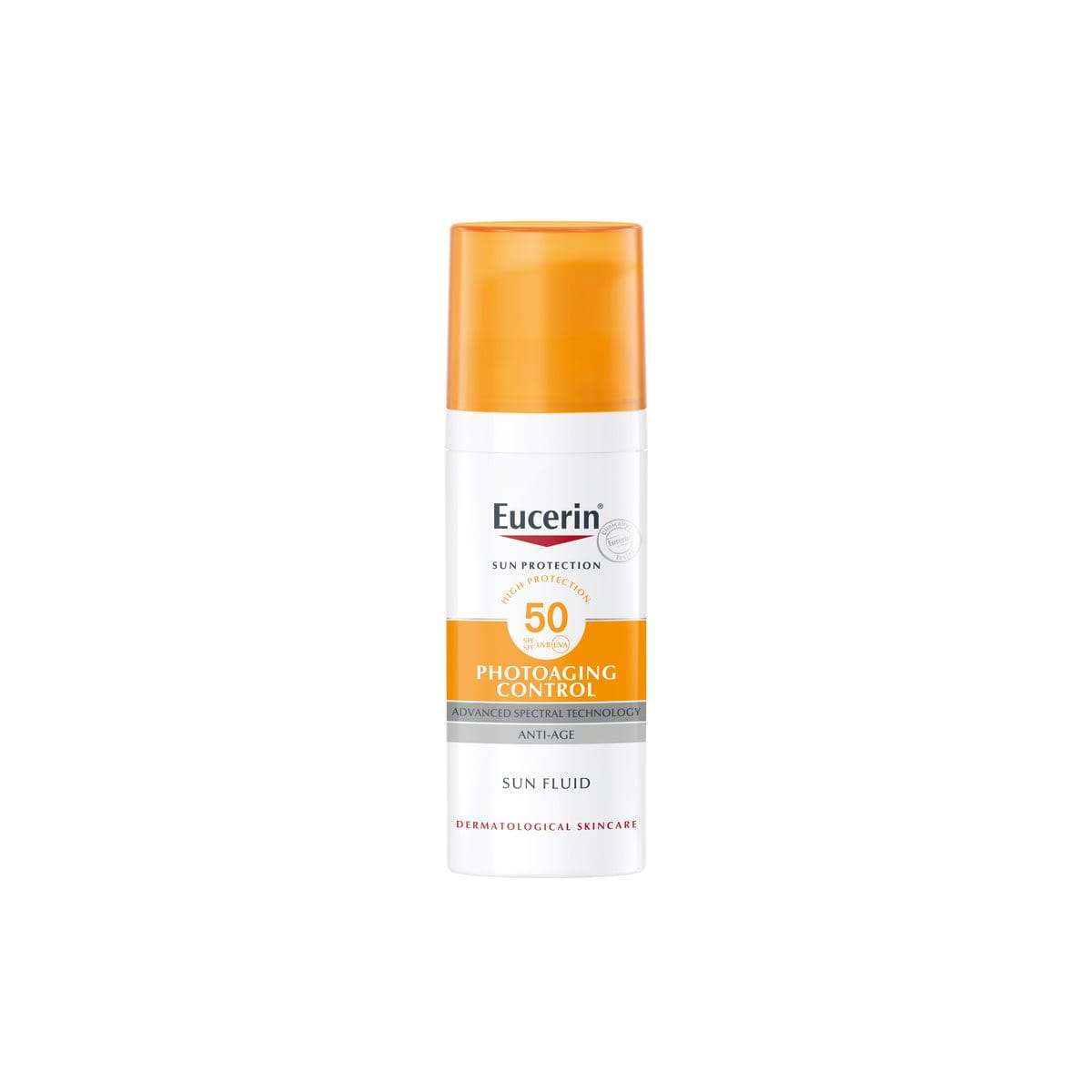
Eucerin Sun Fluid Photoaging Control SPF 50 and Eucerin Sun Face Pigment Control Fluid SPF 50+.
In addition to Eucerin’s Advanced Spectral Technology, the products contain Glycyrrhetinic Acid, which supports the skin’s own DNA repair mechanism, and Hyaluronic Acid, which visibly reduces signs of ageing. The tinted products also contain colour pigments that help to cover uneven pigmentation and instantly unify the complexion. Tinted SPF also works well for applying under and over makeup.
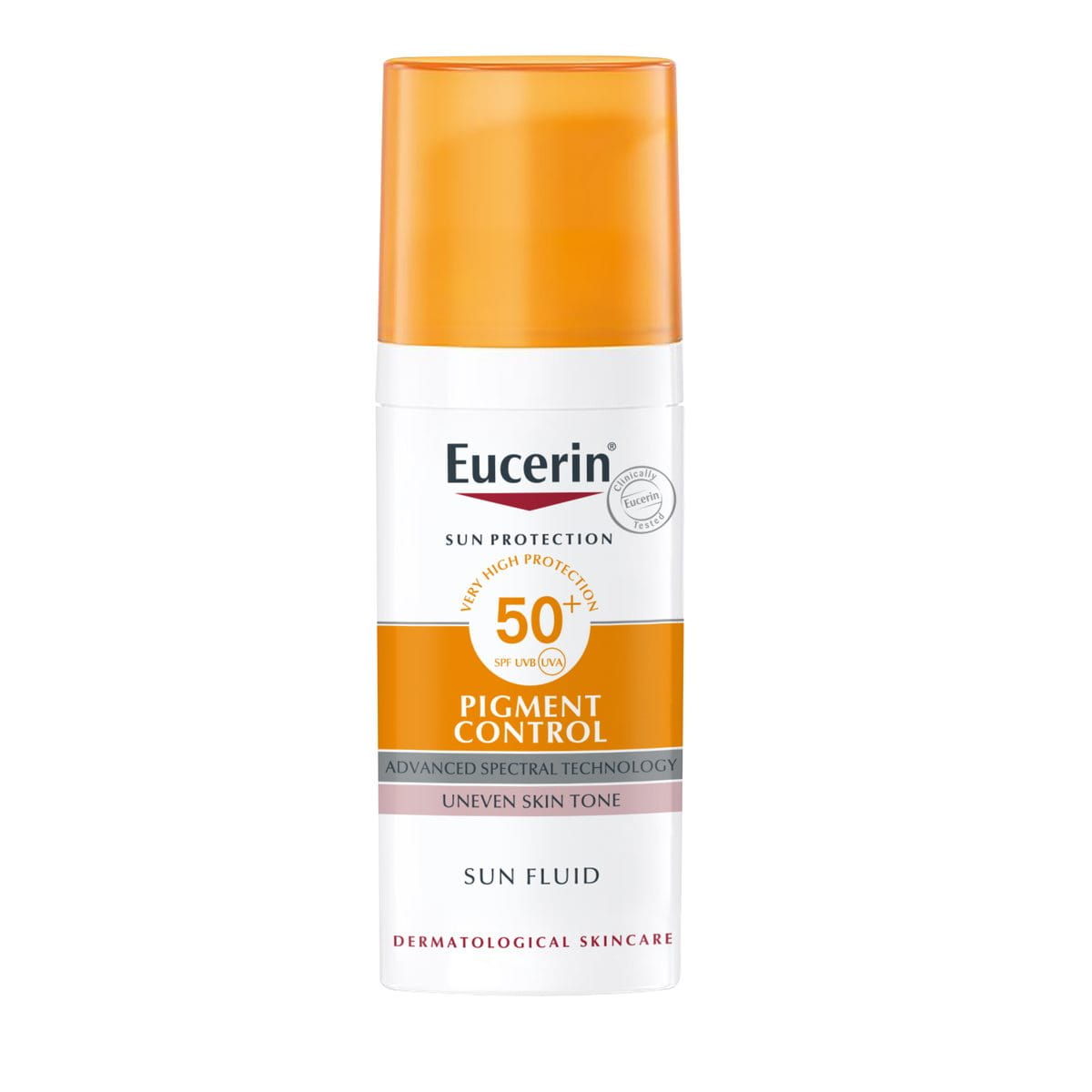
If hyperpigmentation on your face is your primary skin concern, try Eucerin Sun Fluid Pigment Control SPF 50+.
While prevention is best, once you have dark spots, Thiamidol is clinically and dermatologically proven to reduce dark spots and prevent their reappearance.
If you already have pigmentation concerns, such as sun or age spots, the Eucerin Anti-Pigment range is clinically proven to fade them and prevent their reappearance.
You can read more about how to minimise the risks of exposure, how to choose the right sun protection products for your skin, and how best to apply them in Why do I need daily sun protection for my face? And how should I protect my body from the sun?
1 Meeting the highest standards for UVA and UVB protection as defined by Cosmetics Europe. The levels of UVA protection are higher than the EU requirement.
Our brand values

We deliver a holistic dermo-cosmetic approach to protect your skin, keep it healthy and radiant.

For over 100 years, we have dedicated ourselves to researching and innovating in the field of skin science. We believe in creating active ingredients and soothing formulas with high tolerability that work to help you live your life better each day.

We work together with leading dermatologist and pharmacist partners around the world to create innovative and effective skincare products they can trust and recommend.












