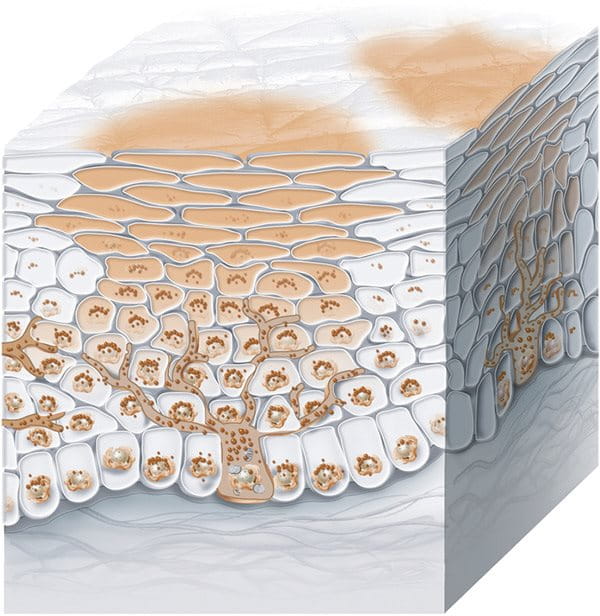
While there are several types of skin pigmentation, the most common ones are age spots, melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and freckles:
Age spots: Also known as sun spots or liver spots, these are caused by exposure to the sun. These normally appear in older adults. For this reason, they appear mainly on body parts that are frequently exposed to UV light, such as the face, neck, décolleté, hands and arms.
Melasma or chloasma: Larger patches of hyperpigmentation develop mainly on the face - specifically the mouth and forehead - though it can also appear on the stomach. Although it can affect both men and women with medium to darker skin, melasma is most common in women with hormone changes, like during pregnancy or when taking birth control medicine. Chloasma usually disappears after pregnancy and after using birth control pills
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: This occurs when a skin injury or trauma heals and leaves a flat area of discolouration behind, usually appearing on the neck or face. It’s commonly found among acne, dermatitis, or eczema sufferers and can also be caused by cosmetic procedures, such as dermabrasion, laser treatment and chemical peels.
Freckles: Freckles are small, flat patches of pigment on the skin, caused by genetics or exposure to the sun. They are harmless and usually found on people with lighter skin tones.
There are other factors that can cause patches of skin to become darker, such as scarring, birthmarks, solar or actinic keratoses and skin cancers, but these aren’t considered to be forms of hyperpigmentation.